Osteoarthritis and Movement

Brain Freeze vs Throat Freeze
September 16, 2024
Nuts vs Chips
September 16, 2024- Accident doctor
- accupuncture
- airplane headache
- alzheimer's
- best habits
- Brain Injuries
- car accident
- car accidents
- cervical strain
- colds
- concussion
- Concussions
- disc bulge
- dosage meds
- dry needling
- dull pain
- E bike injuries
- florida
- good posture
- headaches
- Headrest positions
- Headrest positions after an accident
- Healthy choices
- Healthy flying
- healthy gift guide
- Healthy SPring Ideas
- hip pain
- hyperextension
- injury doctor
- insurance
- Kayaking
- kentucky
- kids motion sickness
- lifestyle
- motion sickness
- neck injury
- no fault insurance doctor
- noise healing
- osteoporosis
- pain symptoms
- pink noise
- posterior chain
- posture
- prevent osteoporosis
- Rest
- Scoliosis
- shoulder pain
- Stress with kids after a motor vehicle accident
- TBI
- tips
- tmj
- torn muscle
- Traumatic Brain Injury
- trigger points
- VitaminD
- What are Post Traumatic headaches?
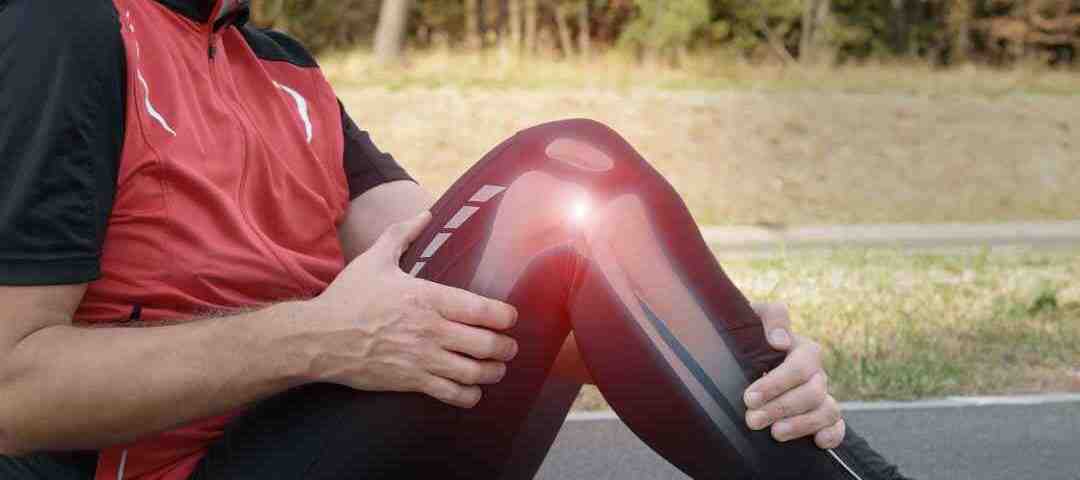
What is Osteoarthritis and How to Keep Moving?
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common and often painful condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a chronic disease characterized by the slow breakdown of tissue that cushions the ends of bones in your joints. This cushion is called cartilage and as it breaks down leads to pain and stiffness. Dr. Aaron Workman, on staff at one of the highest rated car accident medical care facilities in Lexington, Kentucky, addresses the importance of understanding osteoarthritis in order to learn how it is best managed.
The Basics:
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis. The end portions of your bones are surrounded by smooth tough cartilage that can act as a lubricant and a shock absorber. This cartilage can wear away leading to bone rubbing against bone. It primarily affects the joints that bear the most weight, such as the hips, lower back, knees, and hands. The disease can develop due to several factors, including age, genetics, joint injuries, obesity, and repetitive stress. While OA typically is found in specific joints, it can affect many others, but it is just not common. It is most common in older adults.
The symptoms of osteoarthritis typically develop gradually. In the early stages, you might notice mild joint pain or stiffness, especially after physical activity or long periods of inactivity. Over the years, these symptoms can become more severe, leading to chronic pain, swelling, and even a loss of joint function. In more severe cases, the joint can even become deformed leading to even more restrictions in your ability to move and enjoy life.
Treatments:
At this point in time, there is no cure for OA. The disease is progressive, meaning it typically worsens over time. There are treatments and lifestyle changes that can help manage and lessen the symptoms, reduce pain, and improve joint function. Some treatments will involve the combination of medication, some therapies, and lifestyle changes. Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to manage pain and inflammation. In more severe cases, prescription medications or injections may be recommended. Physical therapy can be beneficial as it can be designed to strengthen specific joints which can give more flexibility and therefore likely reduce pain. Another great way to improve mobility is to support the joints while they are active. If you have a painful knee due to OA, wearing knee brace supports on both knees can improve mobility. Orthotics in shoes can serve a similar place by supporting proper posture while moving. For those with more advanced OA surgery may be a last resort treatment when everything else has failed.
Being Proactive:
Staying active is essential for managing osteoarthritis and maintaining joint health. While it may seem counterproductive to exercise when you are in pain, regular physical activity can help reduce stiffness, increase flexibility, and strengthen the muscles around your joints. Activities like swimming, riding a bicycle, and walking are gentle on the joints and give a cardiovascular benefit. Strengthening the muscles around your joints can help reduce the strain on the joints themselves. Stretching exercises can help maintain or improve your range of motion. Yoga is a great example of an activity to increase flexibility and reduce stiffness. Excess weight can place additional stress on weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips. Losing even a small amount of weight can significantly reduce the pressure on your joints.
One of the most important things is keeping a good balance between activity and rest. If you experience pain that lasts for more than a few hours after that activity, then it may be a sign that you need to modify how much you do. OA is a chronic condition, but it does not have to lead to a couch potato lifestyle. By understanding the disease, consulting a healthcare professional, finding appropriate treatment, and becoming proactive with moving, you can manage osteoarthritis effectively and should continue to enjoy a full and active life.
— This article is written by Aaron Workman, DC, one of the members of Chambers Medical Group’s team of car accident chiropractors who offer a variety of treatments and therapies ranging from diagnostic testing to various soft tissue therapies for car accidents and injuries in Kentucky.
- Car Accident Medical Clinic in Tampa
- Car Accident Medical Clinic in Plant City
- Car Accident Medical Clinic in Brandon
- Car Accident Medical Clinic in Lakeland
- Car Accident Medical Clinic in Sarasota
- Car Accident Medical Clinic in Louisville
- Car Accident Medical Clinic in Lexington
- Car Accident Medical Clinic in Florence